Recent advancements in AI have introduced innovative tools like Auto VFX for video editing, Dimension X for creating 3D scenes from images, and Tria for music production, showcasing the technology’s potential to revolutionize various creative fields. Additionally, breakthroughs in surgical robotics and geospatial research tools highlight AI’s transformative impact across healthcare and data analysis.
In a recent update on advancements in artificial intelligence, several groundbreaking tools and models have emerged, showcasing the rapid evolution of AI technology. One of the highlights is Auto VFX, an open-source AI developed by the University of Illinois that allows users to edit videos simply by providing prompts. This tool can add visual effects, insert objects, and even manipulate existing elements in videos with impressive accuracy. For instance, users can prompt the AI to create scenarios like throwing a flaming basketball at a vase or inserting animated characters, demonstrating its potential for revolutionizing film and animation production.
Another remarkable tool introduced is Dimension X, which enables the creation of 3D and 4D scenes from a single image. This AI can extrapolate details and generate realistic camera movements, allowing users to zoom, rotate, and pan around the generated scenes. The tool’s ability to fill in gaps and create consistent visuals from limited data is particularly impressive, making it a valuable asset for filmmakers and content creators who need multiple perspectives without extensive camera setups.
In the realm of music production, a new AI tool called Tria allows users to upload audio samples and create drum beats by simply tapping a rhythm. This innovative approach to music creation could significantly streamline the production process for musicians and producers. Although the code for Tria has not yet been released, it promises to be a useful tool for those looking to enhance their audio projects.
Nvidia has also made strides with its image editing tool, Addit, which allows users to edit images by prompting the AI with specific requests. This tool has shown superior performance compared to existing methods, accurately adding elements to images while maintaining context. The potential applications for this technology are vast, from enhancing personal photos to creating professional-grade images for marketing and design.
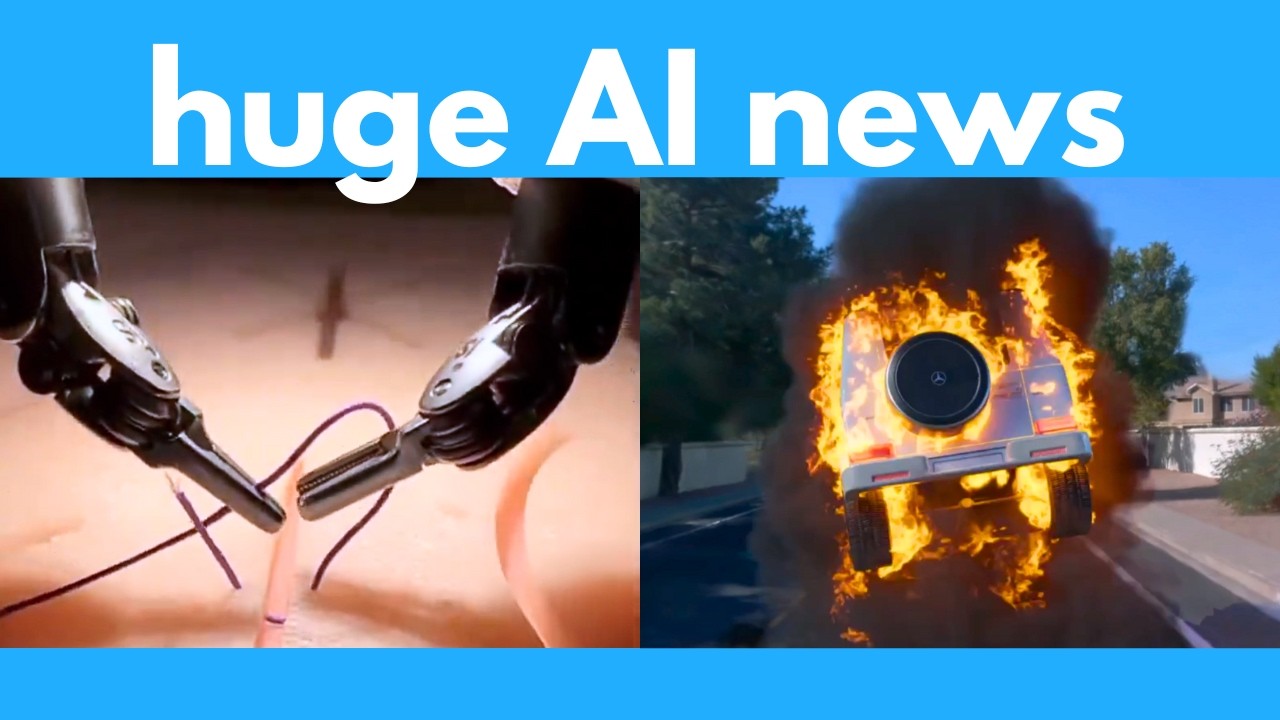
Lastly, significant advancements in AI for surgery have been reported, with researchers at Johns Hopkins developing a surgical robot that learns procedures through imitation learning. This robot has demonstrated the ability to perform surgical tasks with precision comparable to human doctors, indicating a future where robotic assistance could enhance surgical outcomes. Additionally, NASA and Microsoft have collaborated on Earth Co-Pilot, an AI tool designed to simplify geospatial research by allowing users to prompt for specific data, streamlining the process of gathering and analyzing geographical information. Overall, these developments highlight the transformative potential of AI across various fields.