The video by Luke demonstrates how to create a customizable AI voice agent using ElevenLabs for voice synthesis and n8n for workflow automation, enabling tasks like sending emails through voice commands. He guides viewers through setting up webhooks, configuring the AI agent with system prompts and voice cloning, and integrating these components to build a flexible, voice-enabled automation system.
The video by Luke demonstrates how to create a conversational AI voice agent using ElevenLabs and n8n, a workflow automation tool. He begins by showcasing a simple interaction where the AI agent receives a command to send an email, executes the task, and confirms completion. This example illustrates the core concept of integrating voice synthesis with automated workflows to perform tasks like sending emails based on user prompts. Luke emphasizes that this setup is highly customizable and can be expanded for various use cases, including embedding into websites or integrating with company documents for more advanced functionalities.
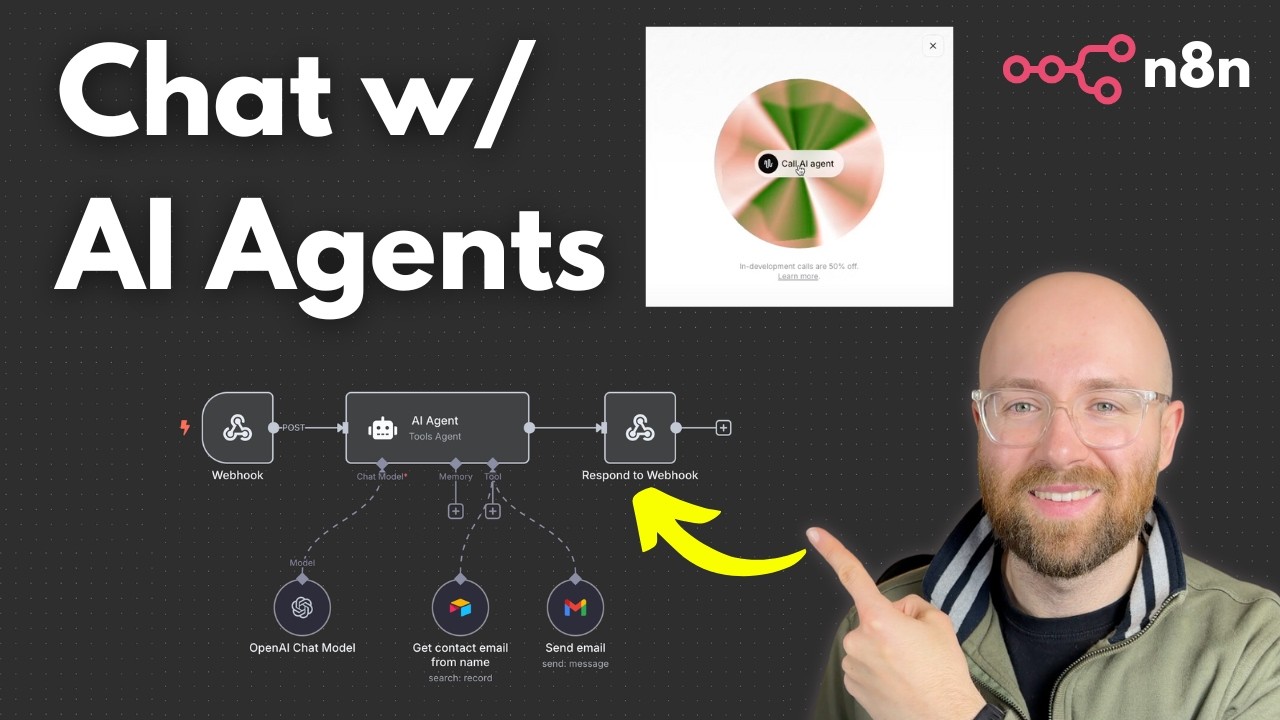
Luke explains the foundational setup involving a webhook, which acts as the entry point for external triggers. The webhook listens for POST requests and initiates the workflow, which then passes data to an AI agent. This agent is configured with a system prompt that defines its role—such as a personal assistant responsible for sending emails—and tools like contact lookup and email sending functions. The workflow retrieves contact information from a database (like Airtable), generates email content, and sends the email through Gmail, completing the automation loop. He highlights the importance of proper configuration and testing to ensure smooth operation.
A significant part of the tutorial covers setting up ElevenLabs for voice synthesis, where Luke shows how to clone a voice or select a pre-made voice for the agent. He guides viewers through creating an agent within ElevenLabs’ platform, defining its initial message, system prompt, and tone. The voice agent can then be called within the workflow, allowing the AI to respond in a natural, human-like voice. Luke stresses the importance of choosing the right language model (like GPT-4 mini) and adjusting parameters such as temperature to balance creativity and accuracy, which impacts how well the AI performs tasks like drafting emails.
The tutorial dives into integrating the voice agent with n8n workflows, including configuring webhooks, tools, and passing parameters such as recipient names and email content. Luke demonstrates how to connect these components, test the entire setup, and troubleshoot issues like ensuring the AI correctly recognizes commands and sends emails. He notes that using the appropriate language models for tool use is crucial, as some models (like GPT-2.0) may not perform well in this context. The process involves detailed steps for setting up API keys, configuring body parameters, and testing the workflow to ensure reliable operation.
In conclusion, Luke emphasizes that this framework is flexible and can be tailored to various needs, such as expanding knowledge bases or integrating with other tools. He encourages viewers to experiment and build upon this foundation to create more sophisticated AI agents. He also promotes his free community resources, templates, and paid courses for those interested in deeper learning and personalized support. Overall, the video provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to building a voice-enabled AI automation system, highlighting its potential for productivity and innovation.