In the video, Evan Edinger explains how to spot AI-generated writing by identifying common red flags such as overuse of M dashes, repetitive sentence structures, vague language, and a lack of personal anecdotes or authentic voice. He emphasizes trusting your intuition or “vibe check” to detect the insincerity and formulaic nature of AI writing, which contrasts with the natural flow and personality found in human-authored content.
In this video, Evan Edinger teaches viewers how to instantly spot AI-generated writing, a skill he believes will be essential by 2025. He begins by highlighting one of the most obvious red flags: the overuse of the M dash punctuation. While the M dash is a legitimate and useful punctuation mark, AI language models like ChatGPT tend to use it far more frequently than humans do, making it a telltale sign of AI writing. Evan explains the difference between hyphens, M dashes, and N dashes, and shares how the M dash has been brought back into popularity by AI, though its presence alone doesn’t confirm AI authorship.
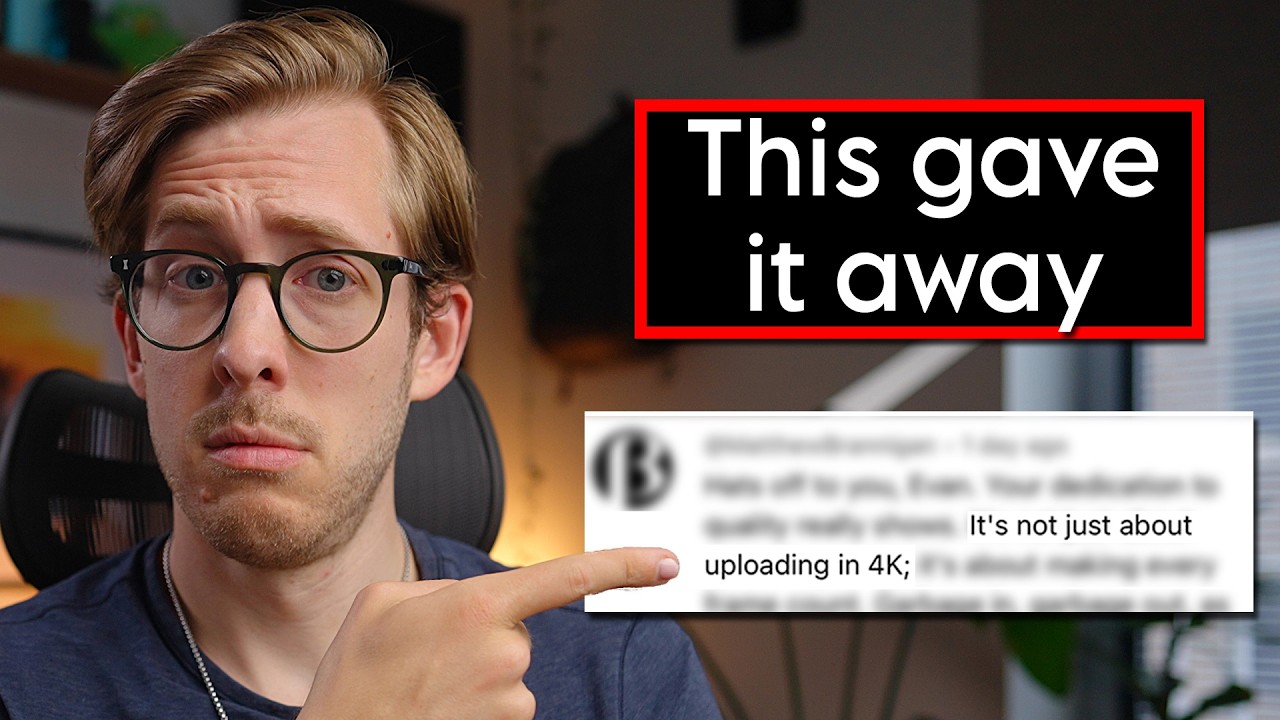
Evan then dives into other common red flags found in AI writing, such as the repetitive use of parallel sentence structures (“It’s not just X, it’s Y”), the frequent appearance of lists of three points, and the tendency to use vague, generic, and overly positive language. He points out that AI writing often feels empty or insincere, filled with jargon and filler words that don’t add real meaning. He also notes that AI-generated content frequently includes strange analogies, excessive clarification, and repeated points, which can make the writing feel unnatural or off.
The video also discusses how AI writing often follows predictable formats, especially on platforms like LinkedIn, where posts tend to have a formulaic structure with hooks, ethos statements, bullet points, and conclusions. Evan highlights that AI-generated comments and posts tend to lack personal anecdotes or unique perspectives, making them feel generic and bland. In contrast, human writing usually includes personal stories, tangents, and a more natural flow that reflects the writer’s personality and experiences.
Evan illustrates these points by comparing two comments he received on a video about jellied eels—one clearly AI-generated and the other genuinely human. The AI comment, despite attempts to disguise itself, contained many of the red flags he described, such as impersonal praise and formulaic phrasing. The human comment, on the other hand, included personal context and a natural tone, making it feel authentic. Evan emphasizes that the best way to detect AI writing is to trust your gut and look for that “vibe check” — the subtle feeling that something is off or insincere.
To conclude, Evan challenges viewers to apply these skills by identifying AI-generated speech in an ad read he performs, revealing afterward which parts were AI-written and which were human. He encourages viewers to share this knowledge widely to help others recognize AI writing. Ultimately, Evan stresses that while AI writing can mimic human language, it struggles to replicate genuine personality and authenticity, which remain the clearest markers of human authorship.