The speaker critiques the rise of artificial intelligence and quantum computing, highlighting their inherent inaccuracies and uncertainties compared to traditional binary computing, which relies on precise ones and zeros. They express concern over the ethical implications and reliability of AI-generated content and the unpredictable nature of qubits in quantum computing, ultimately advocating for the importance of accuracy and reliability in future technological advancements.
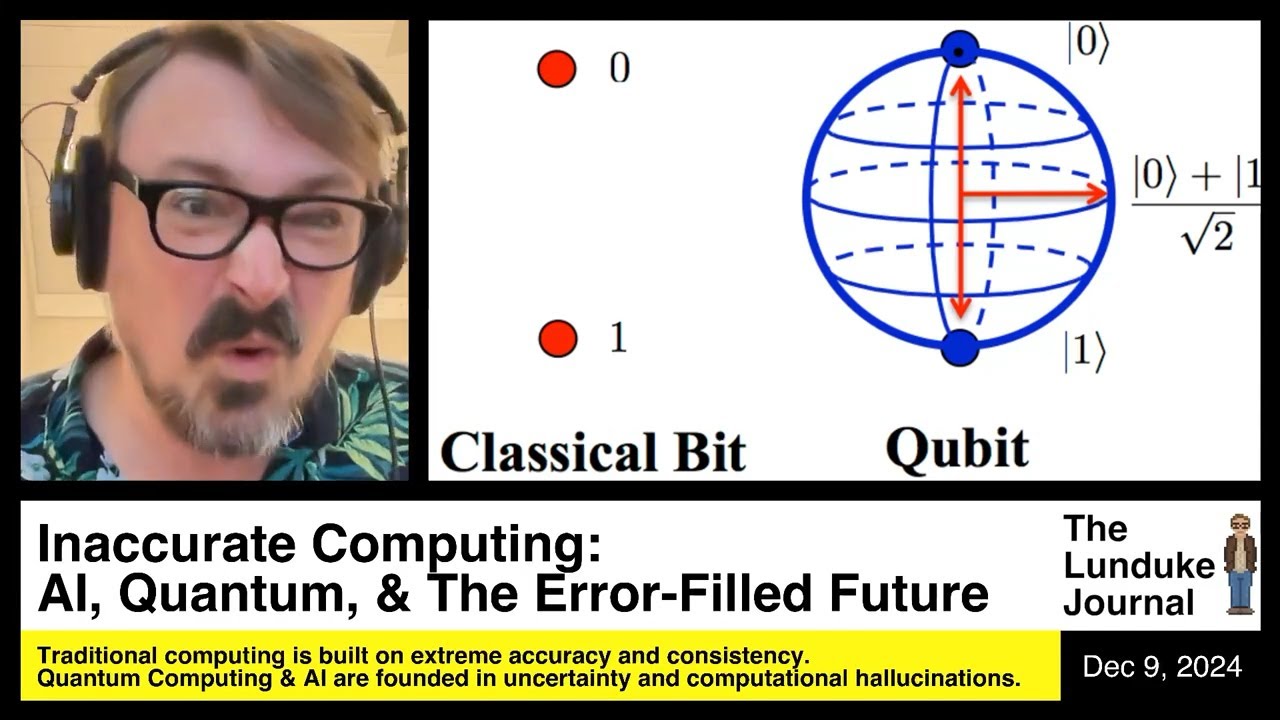
In the video, the speaker expresses a strong aversion to two major advancements in computing: artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing. While acknowledging their technological impressiveness and potential usefulness, the speaker is appalled by the inherent inaccuracies and uncertainties associated with these technologies. They contrast the binary, consistent nature of classical computing, which relies on precise ones and zeros, with the “hallucinatory” and error-prone characteristics of AI and quantum computing. This shift from accuracy to uncertainty is framed as a fundamental departure from the principles that have historically underpinned computing.
The speaker highlights the widespread adoption of AI across various sectors, including tech companies and law enforcement, emphasizing how deeply integrated AI has become in everyday applications. They point out that major corporations are prioritizing AI development, even at the expense of traditional computing methods. The speaker raises concerns about the energy demands of AI data centers, suggesting that the push for AI is leading to drastic measures, such as the construction of nuclear power plants to meet energy needs. This urgency reflects the perceived importance of AI in the future of technology.
The discussion then shifts to the nature of AI itself, describing it as a system designed to generate data that can mislead users into believing it is real. The speaker illustrates this point by referencing AI-generated images and videos, which, despite appearing realistic, are fundamentally fabricated. They argue that the goal of AI is to create convincing illusions rather than provide accurate information, leading to a proliferation of “hallucinated” data that can misinform users. This raises ethical concerns about the reliability of AI-generated content and its implications for society.
Quantum computing is similarly critiqued for its reliance on qubits, which are described as unpredictable and inconsistent compared to classical bits. The speaker explains that qubits can represent multiple states simultaneously, leading to a high degree of error and uncertainty in computations. They provide an example of a project that attempted to run a version of the game Doom on a quantum computer, highlighting the challenges of achieving reliable results due to the inherent instability of qubits. The speaker emphasizes that the current state of quantum computing makes it difficult to trust the accuracy of its outputs.
In conclusion, the speaker expresses skepticism about the future of computing as it increasingly incorporates AI and quantum technologies. They argue that the combination of AI’s hallucinatory nature with the unpredictable behavior of qubits could lead to even greater inaccuracies and inconsistencies. While acknowledging the excitement surrounding these advancements, the speaker remains firmly rooted in the belief that traditional binary computing, with its foundation of accuracy and reliability, is essential for meaningful progress. They invite viewers to consider the implications of these technologies and share their thoughts on the matter.