Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang discussed the increasing energy demands of AI development at the Bipartisan Policy Center, highlighting that future data centers could consume up to 1,000 megawatts of power, necessitating a shift towards renewable energy sources and smarter grid solutions. He emphasized the need for collaboration with policymakers to address these challenges and ensure sustainable growth in the AI industry.
In a recent discussion at the Bipartisan Policy Center in Washington, D.C., Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang addressed the growing energy demands associated with the AI boom. He highlighted the significant strain that AI training processes place on power grids, noting that the trial-and-error nature of developing AI models consumes substantial energy. Huang emphasized that as the industry evolves, the demand for power is expected to increase dramatically, potentially reaching levels several times higher than current consumption.
Huang provided specific figures, stating that data centers today might consume around 100 megawatts of power, but in the future, this could escalate to 1,000 megawatts or more. He pointed out that while this energy demand does not have to be centralized in one location, the sheer volume of data required for training AI models will necessitate increased energy consumption. This trend underscores the importance of addressing energy supply and sustainability in the context of AI development.
To manage the anticipated rise in energy demand, Huang suggested that the industry must pivot towards renewable energy sources. He advocated for the construction of data centers closer to energy sources to enhance efficiency and reduce transmission losses. Additionally, he stressed the need for better collaboration with policymakers to clarify the significance of AI and its energy requirements, ensuring that the industry can effectively address power challenges.
Huang also mentioned the importance of utilizing smart grids, which can optimize energy distribution and usage. By improving the efficiency of energy dispatch, the industry can better accommodate the growing needs of AI technologies. This approach not only addresses immediate energy concerns but also aligns with broader sustainability goals.
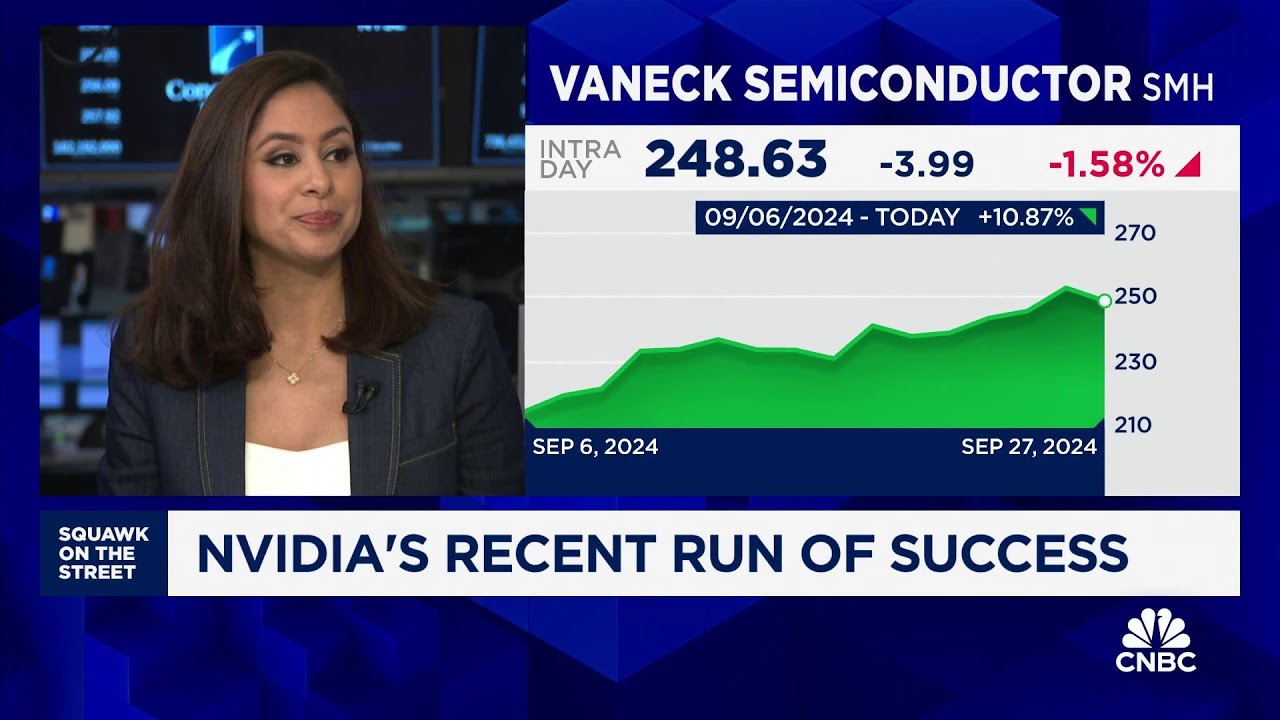
In the context of Nvidia’s recent performance, Huang’s public engagements follow a period of disappointing earnings reported on August 28th. However, since then, Nvidia’s shares have rebounded significantly, rising approximately 12% since early September. The discussion around energy demands and AI is becoming increasingly relevant, especially as companies like GE Vernova, which specializes in smart grids, gain attention on Wall Street, reflecting a growing interest in solutions to the energy challenges posed by the AI sector.