The video explains that Nvidia’s growth is increasingly driven by AI inference, which involves deploying trained models in real-world applications and requires substantial computational power, boosting demand for Nvidia’s GPUs. As companies like Microsoft and Google process trillions of tokens, the surge in inference workloads is positioning it as the key growth engine for Nvidia, shifting focus from geopolitical concerns to global AI deployment.
The video discusses Nvidia’s recent earnings call, highlighting the significant focus on the concept of inference within the AI industry. While China was frequently mentioned during the call, the term “inference” emerged as a key driver of Nvidia’s future growth prospects. The shares of Nvidia are currently experiencing some decline but remain up for the session, reflecting investor interest in this new growth engine.
Deirdre Bosa explains that inference is a crucial and durable driver of Nvidia’s next phase of expansion. The shift in AI development is moving from the initial phase of training models—where the “brain” of AI is built—to the deployment phase, where these models are used in real-world applications. This transition marks a significant change in the AI landscape, emphasizing the importance of inference, which involves applying trained models to generate responses or perform tasks in real time.
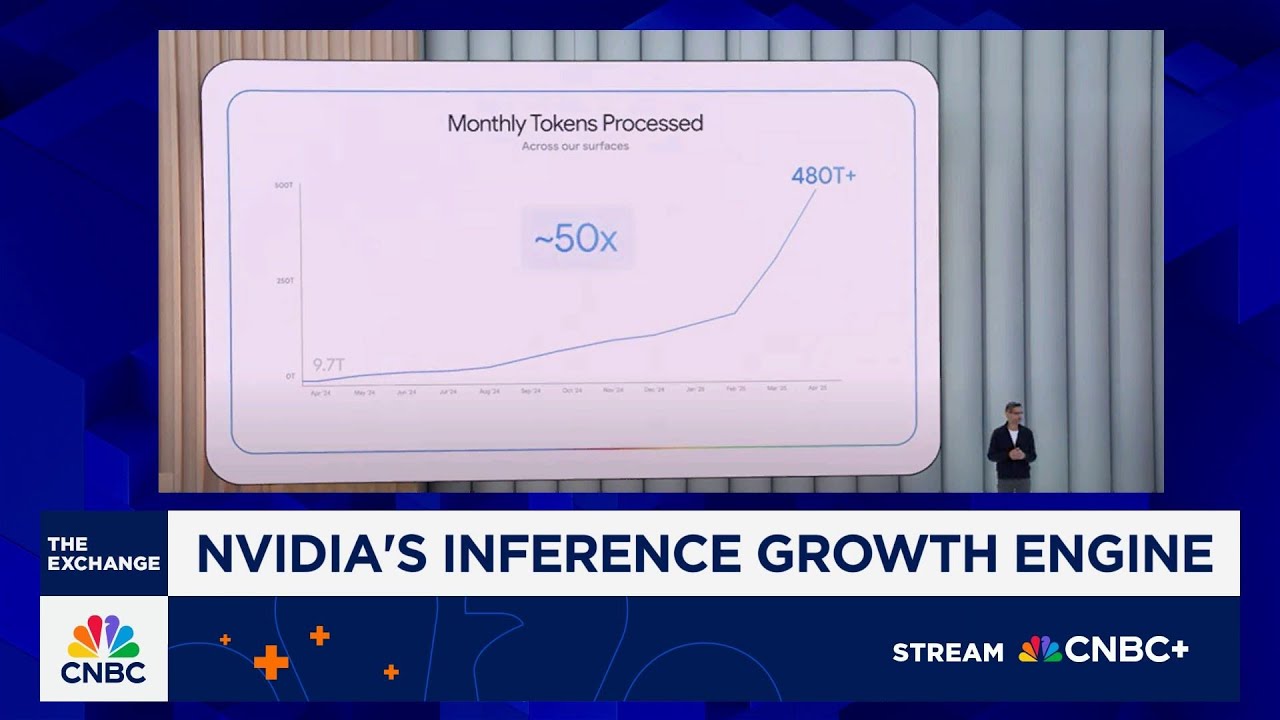
The process of inference involves generating tokens—small chunks of text—each time an AI model responds to a query. As tasks become more complex, the number of tokens processed increases, demanding more computational power. Newer reasoning models that step through answers more carefully are increasing the number of tokens per query, thereby boosting the demand for Nvidia’s GPUs, which dominate this space. This trend is evident in the massive token processing volumes reported by companies like Microsoft and Google, indicating a surge in inference activity.
Microsoft processed over 100 trillion tokens in a single quarter, a fivefold increase year-over-year, illustrating the explosive growth in inference workloads. Similarly, Google’s token usage has shown a parabolic rise, reflecting the widespread integration of AI into consumer and enterprise tools. As these companies embed AI into products used by billions, the demand for Nvidia’s hardware to support inference continues to grow rapidly, fueling a cycle of increasing compute needs.
Finally, Bosa notes that this shift toward inference and real-world AI deployment may reduce the relative impact of geopolitical concerns, such as the China gap. Instead of focusing solely on China, the emphasis is now on the global demand for AI inference, which is becoming a dominant growth engine for Nvidia. This evolving landscape underscores the importance of inference as the next major driver of AI hardware demand and Nvidia’s continued dominance in the sector.