The video demonstrates a biologically inspired spiking neural network that learns arithmetic using Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity (STDP) and dopamine-like delayed rewards, avoiding traditional backpropagation or gradient descent methods. The creator optimizes the network’s hyperparameters with a genetic algorithm and implements the project efficiently using NumPy and Numba, achieving promising results that highlight the potential of biologically plausible learning mechanisms.
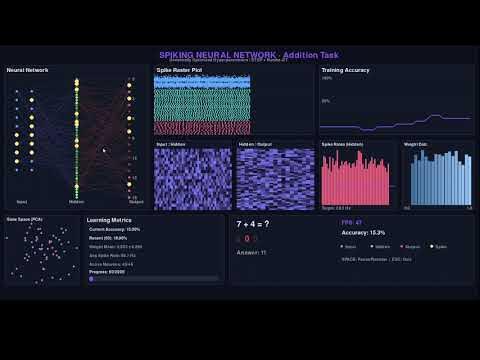
In this video, the creator presents a biologically inspired spiking neural network designed to learn arithmetic without using traditional backpropagation or stochastic gradient descent. Instead, the network learns through Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity (STDP), a learning rule that mimics how synaptic connections in the brain strengthen or weaken based on the timing of neuron spikes. The project is organized into three main files, including a batch-optimized version for fast execution, a Pygame version with a user interface, and a genetic hyperparameter optimization script to fine-tune the network’s many parameters.
The network operates by representing numbers as probabilistic spike trains across 20 input neurons, each neuron having a preference or inclination to fire for certain digits. For example, a neuron might have a high probability of firing when the digit five is presented. These spike trains propagate through hidden neurons and finally to output neurons, which represent the predicted sum in the arithmetic task. The firing of neurons is binary (on or off), but the timing and sequence of spikes are crucial for learning. The network runs multiple cycles per input, and the sequence of neuron activations is tracked to determine which connections contributed to correct or incorrect outputs.
Learning occurs through STDP, where the timing between spikes of connected neurons determines whether the synaptic weight between them is strengthened or weakened. If neuron A fires just before neuron B, the connection is strengthened, while the reverse order weakens it. The network also uses a dopamine-like reward signal that arrives after a delay, modulating the synaptic changes based on whether the output was correct. This delayed reward is managed through eligibility traces, which act as temporary memories of spike correlations, allowing the network to assign credit to the appropriate synapses after the fact.
Because the network has many hyperparameters—such as the number of hidden neurons, firing rates, learning rates, and simulation time—the creator employs a genetic algorithm to optimize these settings. This algorithm simulates natural selection by testing a population of parameter sets, selecting the best performers, and breeding them with crossover and mutation to create new generations. This process has improved the network’s accuracy to around 7-10%, which is above chance level (about 5%) but still far from the performance of conventional neural networks. Despite this, the biologically plausible approach and the use of STDP make the results promising.
The project is implemented using only NumPy and Numba for just-in-time compilation to speed up computations, without relying on deep learning libraries. The creator provides detailed documentation and source code available on Patreon, along with additional resources and community engagement opportunities. Overall, the video offers an insightful look into building a spiking neural network from scratch, emphasizing biological realism and innovative learning mechanisms beyond standard machine learning techniques.