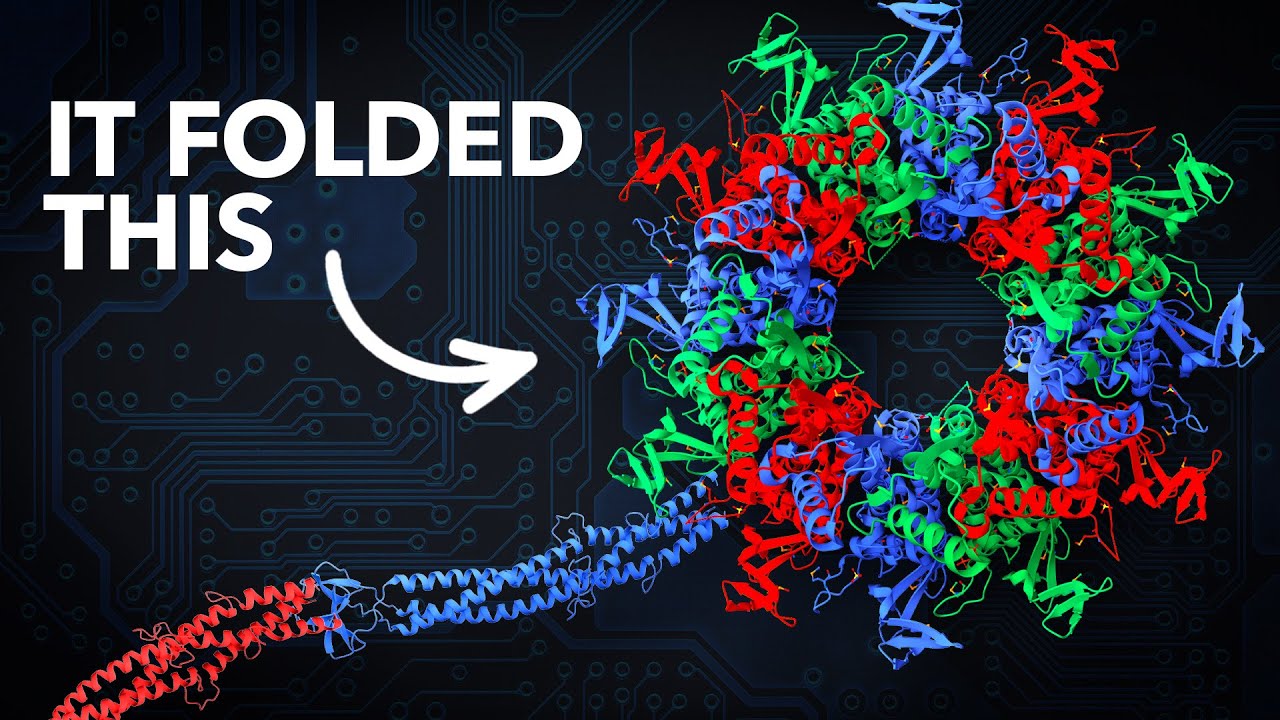
The video highlights the revolutionary impact of AI, particularly through DeepMind’s AlphaFold, which has solved the protein folding problem by predicting the structures of over 200 million proteins, significantly advancing biological research and earning its creators the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. It emphasizes the broader implications of AI in various fields, including materials science and environmental solutions, while also calling for caution regarding its potential risks.
The video discusses a groundbreaking advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) that has the potential to address some of the world’s most pressing problems, such as climate change, disease treatment, and plastic waste disposal. This breakthrough revolves around solving the protein folding problem, which has been a significant challenge in biology for over six decades. While biologists painstakingly determined the structures of around 150,000 proteins, a small team was able to use AI to predict the structures of over 200 million proteins in just a few years, effectively mapping nearly every protein known to exist in nature.
The video explains the fundamental structure of proteins, which are made up of amino acids that fold into specific three-dimensional shapes crucial for their function. Traditional methods of determining protein structures, such as X-ray crystallography, are time-consuming and expensive. The introduction of computational methods, particularly through competitions like CASP (Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction), aimed to leverage computer models to predict protein structures based on their amino acid sequences. Early attempts yielded limited success, but innovations in AI and machine learning began to change the landscape.
One of the pivotal developments in this field was the creation of AlphaFold by DeepMind, which utilized deep learning techniques to predict protein structures. AlphaFold’s initial version, AlphaFold 1, showed promise but was not entirely accurate. The team then developed AlphaFold 2, which incorporated advanced algorithms and a novel architecture called the EVO Former. This model utilized evolutionary data and geometric constraints to significantly improve the accuracy of protein structure predictions, achieving scores that surpassed the traditional benchmarks set by CASP.
The impact of AlphaFold has been profound, accelerating research in various biological fields. It has facilitated the development of vaccines, improved understanding of diseases, and provided insights into the proteins of endangered species. The AlphaFold 2 paper has garnered significant attention, being cited over 30,000 times, and its creators received the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their contributions. This achievement not only highlights the power of AI in biological research but also sets the stage for further advancements in the field.
Looking ahead, the video emphasizes the broader implications of AI in science and technology. The techniques developed for protein folding can be applied to other areas, such as materials science, where AI has already discovered millions of new materials. The potential for AI to unlock new avenues of discovery and innovation is immense, with possibilities ranging from curing diseases to creating sustainable solutions for environmental challenges. The video concludes with a hopeful outlook on the future of AI in science, while also acknowledging the need for caution regarding its potential risks.