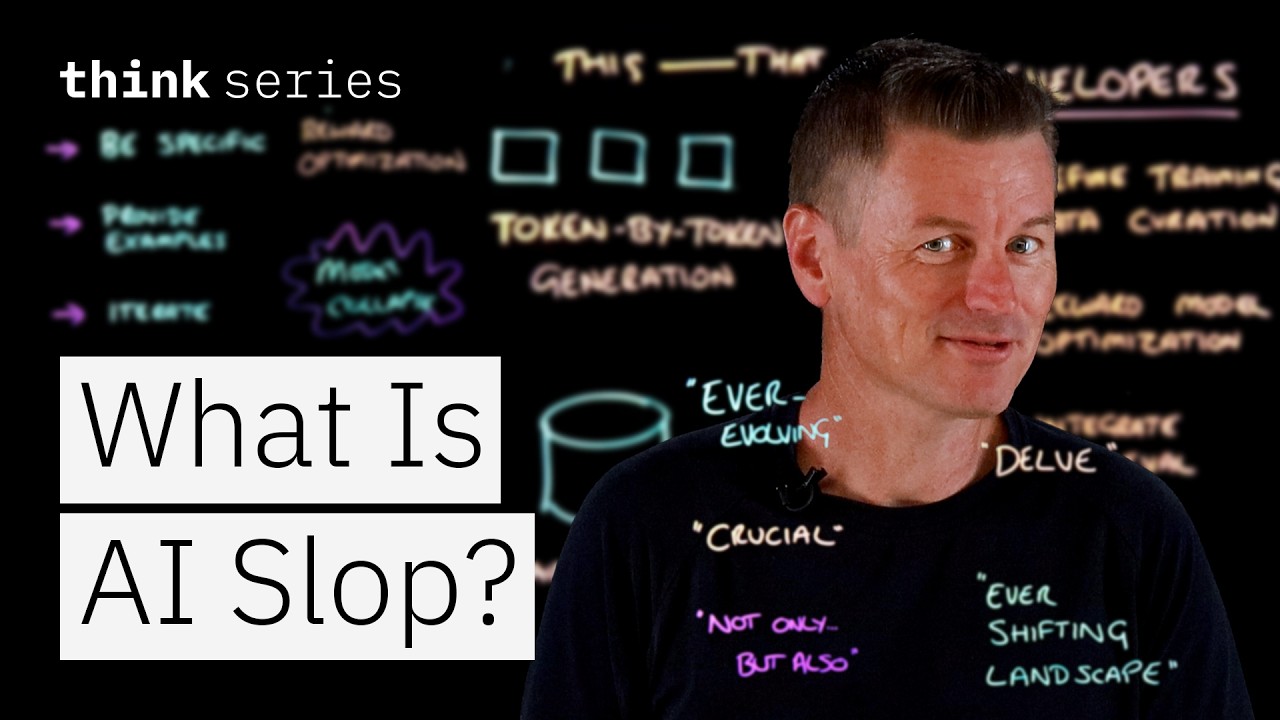
The video explains “AI Slop” as low-quality, formulaic, and error-prone AI-generated content characterized by verbose phrasing and inaccurate or superficial information, often resulting from the limitations and training methods of large language models. It recommends combating AI Slop through precise user prompts, iterative refinement, improved training data, optimized reward models, and integrating retrieval systems to enhance accuracy and value in AI outputs.
The video discusses the concept of “AI Slop,” which refers to low-quality AI-generated content characterized by formulaic, generic, and error-prone text that offers little value. This type of content is pervasive across various platforms, including homework assignments, emails, white papers, and online comments. The presenter highlights how certain words and phrases, like “delve,” have become overused due to AI generation, contributing to the sloppiness. AI Slop can be broken down into two main categories: phrasing and content, both of which exhibit distinctive traits that make the text tedious and unhelpful.
In terms of phrasing, AI Slop often includes inflated and verbose expressions such as “it is important to note that” or formulaic constructs like “not only but also,” which add unnecessary wordiness. Over-the-top adjectives like “ever-evolving” and “game-changing” are common, giving the impression that the text is trying too hard to impress. The frequent and sometimes incorrect use of em dashes without proper spacing is another stylistic quirk that can help identify AI-generated text. These phrasing issues make the content cumbersome to read and detract from its clarity and usefulness.
Content-wise, AI Slop is marked by verbosity, where AI models produce lengthy responses that lack substantive information, similar to a student padding an essay to meet a word count. Another significant problem is the presence of false information or hallucinations, where AI confidently states inaccuracies as facts. This issue is exacerbated by AI content farms that mass-produce SEO-optimized but low-quality articles, flooding the internet with unreliable and repetitive content. The root causes of AI Slop lie in how large language models (LLMs) function, primarily predicting the next word based on statistical patterns rather than aiming for meaningful or goal-driven communication.
The video explains that LLMs are trained on vast datasets that may contain biased or overrepresented phrases, leading to repetitive and generic outputs. Additionally, the reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) process, designed to improve helpfulness, can inadvertently cause “model collapse,” where outputs become overly similar and stylistically narrow. This phenomenon results in a homogenization of AI-generated text, further contributing to the prevalence of AI Slop. Understanding these underlying mechanisms is crucial for addressing the problem effectively.
To combat AI Slop, the video suggests strategies for both users and developers of AI models. Users can improve output quality by crafting specific prompts, providing examples, and iterating on AI responses through conversation to refine the content. Developers, on the other hand, should focus on curating higher-quality training data, optimizing reward models with multiobjective criteria (such as helpfulness, correctness, and brevity), and integrating retrieval systems like RAG to reduce hallucinations by grounding responses in real documents. While AI Slop is widespread, recognizing its signs and applying these strategies can help produce clearer, more accurate, and valuable AI-generated content.